Thiết bị phục vụ phát triển công nghệ
Thiết bị tự động hoá công nghiệp
Linh-phụ kiện cho xe điện
Thiết bị đo lường
Thiết bị văn phòng, IT, Viễn Thông
Thiết bị gia đình










Sử dụng 4 micro kỹ thuật số PDM chất lượng cao, được sắp xếp theo mảng vòng tròn (circular array) để thu thập âm thanh đa hướng.
Tích hợp bộ xử lý giọng nói chuyên dụng XMOS XVF-3000, cung cấp khả năng xử lý âm thanh mạnh mẽ trên bo mạch.
Hỗ trợ các thuật toán quan trọng cho tương tác giọng nói, bao gồm Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC) và Noise Suppression (NS).
Có khả năng xác định hướng giọng nói (Direction of Arrival - DOA) và tập trung thu âm theo hướng đó (Beamforming - BF).
Thiết kế Plug and Play (Cắm và chạy) qua giao diện USB, hoạt động như một thiết bị âm thanh tiêu chuẩn trên nhiều hệ điều hành.
Cho phép thu nhận giọng nói từ xa (Far-field voice capture) với hiệu quả cao, lên đến 5 mét.
Tích hợp 12 đèn LED RGB có thể lập trình, dùng để hiển thị hướng giọng nói (DOA) hoặc trạng thái hoạt động của hệ thống.
 Freeship bán kính TOÀN QUỐC
Freeship bán kính TOÀN QUỐC
Liên hệ hỗ trợ báo giá chi tiết: Hotline: 0378.524.999
Mua hàng tại Showroom Vina Connect Xem đường đi
ReSpeaker Mic Array V2.0 là một giải pháp phát triển phần cứng giúp mở rộng giao tiếp bằng âm thanh (microphone) cho dự án của bạn.
Bo mạch bao gồm các microphone sắp xếp theo hình tròn, có khả năng phát hiện giọng nói cách xa tới 5m ngay cả khi có tạp âm xung quanh.
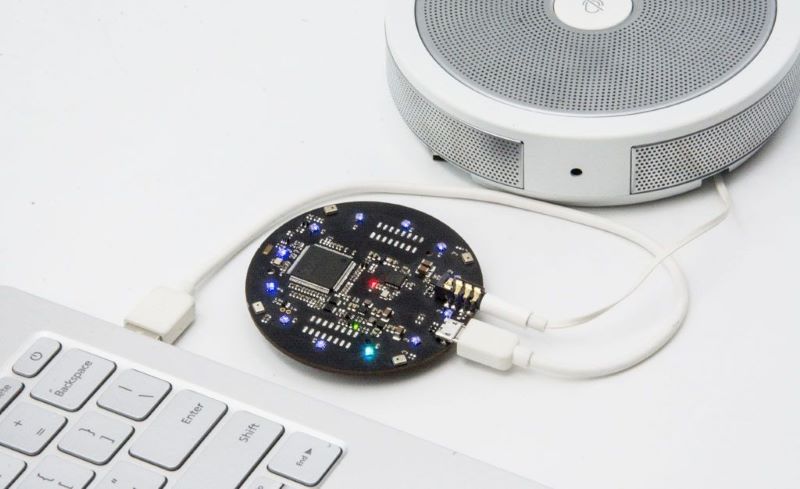

ReSpeaker Mic Array V2.0 được phát triển từ chipset có hiệu suất cao XMOS XVF-3000, gồm nhiều thuật toán nhận dạng giọng nói khác nhau. Bo mạch có thể được gắn chồng lên bo ReSpeaker Core để cải thiện hiệu quả làm việc. Ở phiên bản V2.0 này, microphone cũng đã được cả thiện rất nhiều khi so sánh với phiên bản đầu khi chỉ có 4 microphone.
ReSpeaker Mic Array V2.0 hỗ trợ kết nối USB Audio Class 1.0 (UAC 1.0). Tất cả các hệ điều hành chính bao gồm Windows, macOS và Linux đều tương thích với UAC 1.0, cho phép ReSpeaker Micr Array hoạt động như một sound card mà không cần đến ReSpeaker Core, đồng thời giữ lại các thuật toán xử lý giọng nói như là DoA, BF và AEC.
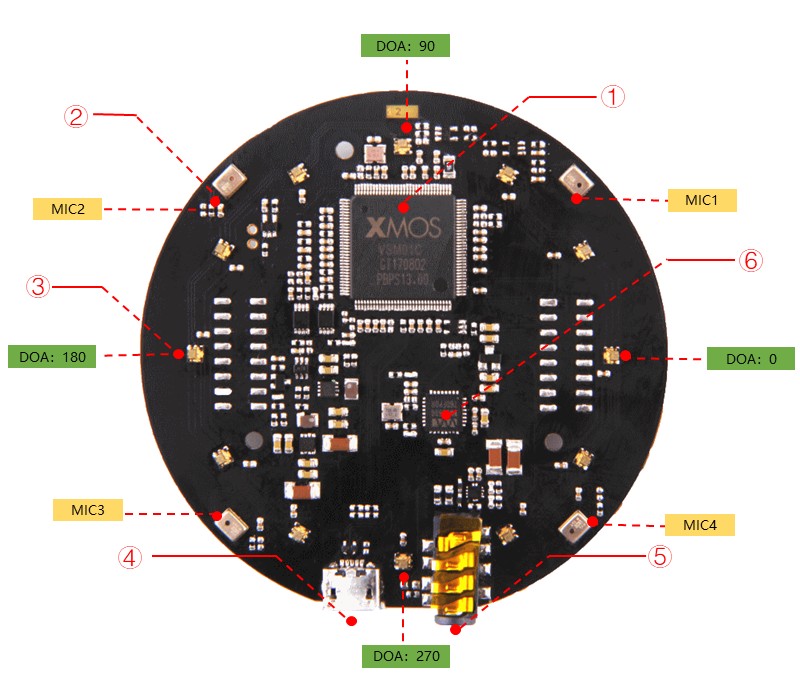
① XMOS XVF-3000: Tích hợp các thuật toán DSP gồm loại bỏ tiếng vọng âm thanh (AEC), định dạng chùm tia, hiện tượng phá âm, giảm tiếng ồn và điều chỉnh khuếch đại.
② Micro kỹ thuật số: The MP34DT01-M là micro MEMS kỹ thuật số siêu nhỏ gọn, công suất thấp, đa hướng được xây dựng với phần tử cảm biến điện dung và giao diện IC.
③ RGB LED: RGB LED ba màu.
④ Cổng USB : Cung cấp nguồn và điều khiển mic array.
⑤ Jack cắm tai nghe 3.5mm: Chúng ta có thể cắm loa hoặc tai nghe đang hoạt động vào cổng này.
⑥ WM8960: The WM8960 là codec âm thanh nổi công suất thấp có trình điều khiển loa Class D để cung cấp 1W cho mỗi kênh thành 8W.



Ứng dụng:
Thời hạn bảo hành: 12 tháng

The ReSpeaker Mic Array v2.0 is an upgrade to the original ReSpeaker Mic Array v1.0. This upgraded version is based on XMOS’s XVF-3000, a significantly higher performing chipset than the previously used XVSM-2000. This new chipset includes many voice recognition algorithms to assist in performance. The array can be stacked (connected) right onto the top of the original ReSpeaker Core to significantly improve the voice interaction performance.The microphones have also been improved in this version allowing significant performance improvements over the first generation mic array with only 4 microphones.
The ReSpeaker Mic Array v2.0 supports USB Audio Class 1.0 (UAC 1.0) directly. All major Operating System, including Windows,macOS, and Linux are compatible with UAC 1.0, allowing the mic array to function as a sound card without the ReSpeaker Core,while also retaining voice algorithms, such as DoA, BF, and AEC on those systems.
The ReSpeaker Mic Array v2.0 is a great solution for those who wish to add voice interface into their existing products or future products. It also works well as an entry point to higher level voice interface evaluation. The board allows some flexibility for customization upon request.
The ReSpeaker Mic Array v2.0 has two firmware versions available, one including speech algorithms and a second for raw voice data.
| Product Version | Changes | Released Date |
|---|---|---|
| ReSpeaker Mic Array v1.0 | Initial | Aug 15, 2016 |
| ReSpeaker Mic Array v2.0 | XVSM-2000 is EOL,change MCU to XVF-3000 and reduce the Mics from 7 to 4. | Jan 25, 2018 |

① XMOS XVF-3000: It integrates advanced DSP algorithms that include Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC), beamforming, dereverberation, noise suppression and gain control.
② Digital Microphone: The MP34DT01-M is an ultra-compact, lowpower, omnidirectional, digital MEMS microphone built with a capacitive sensing element and an IC interface.
③ RGB LED: Three-color RGB LED.
④ USB Port: Provide the power and control the mic array.
⑤ 3.5mm Headphone jack: Output audio, We can plug active speakers or Headphones into this port.
⑥ WM8960: The WM8960 is a low power stereo codec featuring Class D speaker drivers to provide 1 W per channel into 8 W loads.
System Diagram 
Pin Map 
Dimensions 

ReSpeaker Mic Array v2.0 is compatiable with Windows, Mac, Linux systems andriod. The below scripts are tested on Python2.7.
For andriod, we tested it with emteria.OS(andriod 7.1) on Raspberry. We plug the mic array v2.0 to raspberry pi USB port and select the ReSpeaker mic array v2.0 as audio device. Here is the audio recording screen.

Here is the audio playing screen. We plug speaker to ReSpeaker mic array v2.0 3.5mm audio jack and hear what we record.

There are 2 firmwares. One includes 1 channel data, while the other inlcudes 6 channels data (factory firmware). Here is the table for the differences.
| Firmware | Channels | Note |
|---|---|---|
| 1_channel_firmware.bin | 1 | Processed audio for ASR |
| 6_channels_firmware.bin | 6 | Channel 0: processed audio for ASR Channel 1: mic1 raw data Channel 2: mic2 raw data Channel 3: mic3 raw data Channel 4: mic4 raw data Channel 5: merged playback |
For Linux: The Mic array supports the USB DFU. We develop a python script dfu.py to update the firmware through USB.
sudo apt-get update
sudo pip install pyusb click
git clone https://github.com/respeaker/usb_4_mic_array.git
cd usb_4_mic_array
sudo python dfu.py --download 6_channels_firmware.bin # The 6 channels version
# if you want to use 1 channel,then the command should be like:
sudo python dfu.py --download 1_channel_firmware.bin
Here is the firmware downloading result. 
For Windows/Mac: We do not suggest use Windows/Mac and Linux vitual machine to update the firmware.
Here is the Acoustic Echo Cancellation example with 6 channels firmware.


Channel0 Audio(processed by algorithms):
Channel1 Audio(Mic1 raw data):
Channel5 Audio(Playback data):
Here is the video about the DOA and AEC.
SEEED DFU and SEEED Control (ReSpeaker Mic Array has 2 devices on Windows Device Manager).
Please make sure that libusb-win32 is selected, not WinUSB or libusbK.
For Linux/Mac/Windows: We can configure some parameters of built-in algorithms.
git clone https://github.com/respeaker/usb_4_mic_array.git
cd usb_4_mic_array
python tuning.py -p
python tuning.py AGCONOFF 0
pi@raspberrypi:~/usb_4_mic_array $ sudo python tuning.py DOAANGLE
DOAANGLE: 180
We can control the ReSpeaker Mic Array V2's LEDs through USB. The USB device has a Vendor Specific Class Interface which can be used to send data through USB Control Transfer. We refer pyusb python library and come out the usb_pixel_ring python library.
The LED control command is sent by pyusb's usb.core.Device.ctrl_transfer(), its parameters as below:
ctrl_transfer(usb.util.CTRL_OUT | usb.util.CTRL_TYPE_VENDOR | usb.util.CTRL_RECIPIENT_DEVICE, 0, command, 0x1C, data, TIMEOUT)
Here are the usb_pixel_ring APIs.
| Command | Data | API | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | [0] | pixel_ring.trace() | trace mode, LEDs changing depends on VADand DOA |
| 1 | [red, green, blue, 0] | pixel_ring.mono() | mono mode, set all RGB LED to a single color, for example Red(0xFF0000), Green(0x00FF00), Blue(0x0000FF) |
| 2 | [0] | pixel_ring.listen() | listen mode, similar with trace mode, but not turn LEDs off |
| 3 | [0] | pixel_ring.speak() | wait mode |
| 4 | [0] | pixel_ring.think() | speak mode |
| 5 | [0] | pixel_ring.spin() | spin mode |
| 6 | [r, g, b, 0] * 12 | pixel_ring.custimize() | custom mode, set each LED to its own color |
| 0x20 | [brightness] | pixel_ring.set_brightness() | set brightness, range: 0x00~0x1F |
| 0x21 | [r1, g1, b1, 0, r2, g2, b2, 0] | pixel_ring.set_color_palette() | set color palette, for example, pixel_ring.set_color_palette(0xff0000, 0x00ff00) together with pixel_ring.think() |
| 0x22 | [vad_led] | pixel_ring.set_vad_led() | set center LED: 0 - off, 1 - on, else - depends on VAD |
| 0x23 | [volume] | pixel_ring.set_volume() | show volume, range: 0 ~ 12 |
| 0x24 | [pattern] | pixel_ring.change_pattern() | set pattern, 0 - Google Home pattern, others - Echo pattern |
For Linux: Here is the example to control the leds. Please follow below commands to run the demo.
git clone https://github.com/respeaker/pixel_ring.git
cd pixel_ring
sudo python setup.py install
sudo python examples/usb_mic_array.py
Here is the code of the usb_mic_array.py.
import time
from pixel_ring import pixel_ring
if __name__ == '__main__':
pixel_ring.change_pattern('echo')
while True:
try:
pixel_ring.wakeup()
time.sleep(3)
pixel_ring.think()
time.sleep(3)
pixel_ring.speak()
time.sleep(6)
pixel_ring.off()
time.sleep(3)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
break
pixel_ring.off()
time.sleep(1)
For Windows/Mac: Here is the example to control the leds.
git clone https://github.com/respeaker/pixel_ring.git
cd pixel_ring/pixel_ring
from usb_pixel_ring_v2 import PixelRing
import usb.core
import usb.util
import time
dev = usb.core.find(idVendor=0x2886, idProduct=0x0018)
print dev
if dev:
pixel_ring = PixelRing(dev)
while True:
try:
pixel_ring.wakeup(180)
time.sleep(3)
pixel_ring.listen()
time.sleep(3)
pixel_ring.think()
time.sleep(3)
pixel_ring.set_volume(8)
time.sleep(3)
pixel_ring.off()
time.sleep(3)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
break
pixel_ring.off()
If you see "None" printed on screen, please reinstall the libusb-win32 driver.
For Windows/Mac/Linux: Here is the example to view the DOA. The Green LED is the indicator of the voice direction. For the angle, please refer to hardware overview.
git clone https://github.com/respeaker/usb_4_mic_array.git
cd usb_4_mic_array
from tuning import Tuning
import usb.core
import usb.util
import time
dev = usb.core.find(idVendor=0x2886, idProduct=0x0018)
if dev:
Mic_tuning = Tuning(dev)
print Mic_tuning.direction
while True:
try:
print Mic_tuning.direction
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
break
pi@raspberrypi:~/usb_4_mic_array $ sudo python doa.py
184
183
175
105
104
104
103
For Windows/Mac/Linux: Here is the example to view the VAD. The Red LED is the indicator of the VAD.
git clone https://github.com/respeaker/usb_4_mic_array.git
cd usb_4_mic_array
from tuning import Tuning
import usb.core
import usb.util
import time
dev = usb.core.find(idVendor=0x2886, idProduct=0x0018)
#print dev
if dev:
Mic_tuning = Tuning(dev)
print Mic_tuning.is_voice()
while True:
try:
print Mic_tuning.is_voice()
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
break
pi@raspberrypi:~/usb_4_mic_array $ sudo python VAD.py
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
For the threshold of VAD, we also can use the GAMMAVAD_SR to set. Please refer to Tuning for more detail.
We use PyAudio python library to extract voice through USB.
For Linux: We can use below commands to record or play the voice.
arecord -D plughw:1,0 -f cd test.wav # record, please use the arecord -l to check the card and hardware first
aplay -D plughw:1,0 -f cd test.wav # play, please use the aplay -l to check the card and hardware first
arecord -D plughw:1,0 -f cd |aplay -D plughw:1,0 -f cd # record and play at the same time
We also can use python script to extract voice.
sudo pip install pyaudio
cd ~
nano get_index.py
import pyaudio
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
info = p.get_host_api_info_by_index(0)
numdevices = info.get('deviceCount')
for i in range(0, numdevices):
if (p.get_device_info_by_host_api_device_index(0, i).get('maxInputChannels')) > 0:
print "Input Device id ", i, " - ", p.get_device_info_by_host_api_device_index(0, i).get('name')
Step 3, press Ctrl + X to exit and press Y to save.
Step 4, run 'sudo python get_index.py' and we will see the device ID as below.
Input Device id 2 - ReSpeaker 4 Mic Array (UAC1.0): USB Audio (hw:1,0)
RESPEAKER_INDEX = 2 to index number. Run python script record.py to record a speech.
import pyaudio
import wave
RESPEAKER_RATE = 16000
RESPEAKER_CHANNELS = 6 # change base on firmwares, 1_channel_firmware.bin as 1 or 6_channels_firmware.bin as 6
RESPEAKER_WIDTH = 2
# run getDeviceInfo.py to get index
RESPEAKER_INDEX = 2 # refer to input device id
CHUNK = 1024
RECORD_SECONDS = 5
WAVE_OUTPUT_FILENAME = "output.wav"
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(
rate=RESPEAKER_RATE,
format=p.get_format_from_width(RESPEAKER_WIDTH),
channels=RESPEAKER_CHANNELS,
input=True,
input_device_index=RESPEAKER_INDEX,)
print("* recording")
frames = []
for i in range(0, int(RESPEAKER_RATE / CHUNK * RECORD_SECONDS)):
data = stream.read(CHUNK)
frames.append(data)
print("* done recording")
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
p.terminate()
wf = wave.open(WAVE_OUTPUT_FILENAME, 'wb')
wf.setnchannels(RESPEAKER_CHANNELS)
wf.setsampwidth(p.get_sample_size(p.get_format_from_width(RESPEAKER_WIDTH)))
wf.setframerate(RESPEAKER_RATE)
wf.writeframes(b''.join(frames))
wf.close()
import pyaudio
import wave
import numpy as np
RESPEAKER_RATE = 16000
RESPEAKER_CHANNELS = 6 # change base on firmwares, 1_channel_firmware.bin as 1 or 6_channels_firmware.bin as 6
RESPEAKER_WIDTH = 2
# run getDeviceInfo.py to get index
RESPEAKER_INDEX = 3 # refer to input device id
CHUNK = 1024
RECORD_SECONDS = 3
WAVE_OUTPUT_FILENAME = "output.wav"
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(
rate=RESPEAKER_RATE,
format=p.get_format_from_width(RESPEAKER_WIDTH),
channels=RESPEAKER_CHANNELS,
input=True,
input_device_index=RESPEAKER_INDEX,)
print("* recording")
frames = []
for i in range(0, int(RESPEAKER_RATE / CHUNK * RECORD_SECONDS)):
data = stream.read(CHUNK)
# extract channel 0 data from 6 channels, if you want to extract channel 1, please change to [1::6]
a = np.fromstring(data,dtype=np.int16)[0::6]
frames.append(a.tostring())
print("* done recording")
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
p.terminate()
wf = wave.open(WAVE_OUTPUT_FILENAME, 'wb')
wf.setnchannels(1)
wf.setsampwidth(p.get_sample_size(p.get_format_from_width(RESPEAKER_WIDTH)))
wf.setframerate(RESPEAKER_RATE)
wf.writeframes(b''.join(frames))
wf.close()
For Windows:
pip install pyaudio
C:\Users\XXX\Desktop>python get_index.py
Input Device id 0 - Microsoft Sound Mapper - Input
Input Device id 1 - ReSpeaker 4 Mic Array (UAC1.0)
Input Device id 2 - Internal Microphone (Conexant I)
C:\Users\XXX\Desktop>python record.py
* recording
* done recording
If we see "Error: %1 is not a valid Win32 application.", please install Python Win32 version.
For MAC:
pip install pyaudio
MacBook-Air:Desktop XXX$ python get_index.py
Input Device id 0 - Built-in Microphone
Input Device id 2 - ReSpeaker 4 Mic Array (UAC1.0)
MacBook-Air:Desktop XXX$ python record.py
2018-03-24 14:53:02.400 Python[2360:16629] 14:53:02.399 WARNING: 140: This application, or a library it uses, is using the deprecated Carbon Component Manager for hosting Audio Units. Support for this will be removed in a future release. Also, this makes the host incompatible with version 3 audio units. Please transition to the API's in AudioComponent.h.
* recording
* done recording
Q1: Parameters of built-in algorithms
pi@raspberrypi:~/usb_4_mic_array $ python tuning.py -p
name type max min r/w info
-------------------------------
AECFREEZEONOFF int 1 0 rw Adaptive Echo Canceler updates inhibit.
0 = Adaptation enabled
1 = Freeze adaptation, filter only
AECNORM float 16 0.25 rw Limit on norm of AEC filter coefficients
AECPATHCHANGE int 1 0 ro AEC Path Change Detection.
0 = false (no path change detected)
1 = true (path change detected)
AECSILENCELEVEL float 1 1e-09 rw Threshold for signal detection in AEC [-inf .. 0] dBov (Default: -80dBov = 10log10(1x10-8))
AECSILENCEMODE int 1 0 ro AEC far-end silence detection status.
0 = false (signal detected)
1 = true (silence detected)
AGCDESIREDLEVEL float 0.99 1e-08 rw Target power level of the output signal.
[−inf .. 0] dBov (default: −23dBov = 10log10(0.005))
AGCGAIN float 1000 1 rw Current AGC gain factor.
[0 .. 60] dB (default: 0.0dB = 20log10(1.0))
AGCMAXGAIN float 1000 1 rw Maximum AGC gain factor.
[0 .. 60] dB (default 30dB = 20log10(31.6))
AGCONOFF int 1 0 rw Automatic Gain Control.
0 = OFF
1 = ON
AGCTIME float 1 0.1 rw Ramps-up / down time-constant in seconds.
CNIONOFF int 1 0 rw Comfort Noise Insertion.
0 = OFF
1 = ON
DOAANGLE int 359 0 ro DOA angle. Current value. Orientation depends on build configuration.
ECHOONOFF int 1 0 rw Echo suppression.
0 = OFF
1 = ON
FREEZEONOFF int 1 0 rw Adaptive beamformer updates.
0 = Adaptation enabled
1 = Freeze adaptation, filter only
FSBPATHCHANGE int 1 0 ro FSB Path Change Detection.
0 = false (no path change detected)
1 = true (path change detected)
FSBUPDATED int 1 0 ro FSB Update Decision.
0 = false (FSB was not updated)
1 = true (FSB was updated)
GAMMAVAD_SR float 1000 0 rw Set the threshold for voice activity detection.
[−inf .. 60] dB (default: 3.5dB 20log10(1.5))
GAMMA_E float 3 0 rw Over-subtraction factor of echo (direct and early components). min .. max attenuation
GAMMA_ENL float 5 0 rw Over-subtraction factor of non-linear echo. min .. max attenuation
GAMMA_ETAIL float 3 0 rw Over-subtraction factor of echo (tail components). min .. max attenuation
GAMMA_NN float 3 0 rw Over-subtraction factor of non- stationary noise. min .. max attenuation
GAMMA_NN_SR float 3 0 rw Over-subtraction factor of non-stationary noise for ASR.
[0.0 .. 3.0] (default: 1.1)
GAMMA_NS float 3 0 rw Over-subtraction factor of stationary noise. min .. max attenuation
GAMMA_NS_SR float 3 0 rw Over-subtraction factor of stationary noise for ASR.
[0.0 .. 3.0] (default: 1.0)
HPFONOFF int 3 0 rw High-pass Filter on microphone signals.
0 = OFF
1 = ON - 70 Hz cut-off
2 = ON - 125 Hz cut-off
3 = ON - 180 Hz cut-off
MIN_NN float 1 0 rw Gain-floor for non-stationary noise suppression.
[−inf .. 0] dB (default: −10dB = 20log10(0.3))
MIN_NN_SR float 1 0 rw Gain-floor for non-stationary noise suppression for ASR.
[−inf .. 0] dB (default: −10dB = 20log10(0.3))
MIN_NS float 1 0 rw Gain-floor for stationary noise suppression.
[−inf .. 0] dB (default: −16dB = 20log10(0.15))
MIN_NS_SR float 1 0 rw Gain-floor for stationary noise suppression for ASR.
[−inf .. 0] dB (default: −16dB = 20log10(0.15))
NLAEC_MODE int 2 0 rw Non-Linear AEC training mode.
0 = OFF
1 = ON - phase 1
2 = ON - phase 2
NLATTENONOFF int 1 0 rw Non-Linear echo attenuation.
0 = OFF
1 = ON
NONSTATNOISEONOFF int 1 0 rw Non-stationary noise suppression.
0 = OFF
1 = ON
NONSTATNOISEONOFF_SR int 1 0 rw Non-stationary noise suppression for ASR.
0 = OFF
1 = ON
RT60 float 0.9 0.25 ro Current RT60 estimate in seconds
RT60ONOFF int 1 0 rw RT60 Estimation for AES. 0 = OFF 1 = ON
SPEECHDETECTED int 1 0 ro Speech detection status.
0 = false (no speech detected)
1 = true (speech detected)
STATNOISEONOFF int 1 0 rw Stationary noise suppression.
0 = OFF
1 = ON
STATNOISEONOFF_SR int 1 0 rw Stationary noise suppression for ASR.
0 = OFF
1 = ON
TRANSIENTONOFF int 1 0 rw Transient echo suppression.
0 = OFF
1 = ON
VOICEACTIVITY int 1 0 ro VAD voice activity status.
0 = false (no voice activity)
1 = true (voice activity)
Q2: ImportError: No module named usb.core
A2: Run sudo pip install pyusb to install the pyusb.
pi@raspberrypi:~/usb_4_mic_array $ sudo python tuning.py DOAANGLE
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "tuning.py", line 5, in <module>
import usb.core
ImportError: No module named usb.core
pi@raspberrypi:~/usb_4_mic_array $ sudo pip install pyusb
Collecting pyusb
Downloading pyusb-1.0.2.tar.gz (54kB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 61kB 101kB/s
Building wheels for collected packages: pyusb
Running setup.py bdist_wheel for pyusb ... done
Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/8b/7f/fe/baf08bc0dac02ba17f3c9120f5dd1cf74aec4c54463bc85cf9
Successfully built pyusb
Installing collected packages: pyusb
Successfully installed pyusb-1.0.2
pi@raspberrypi:~/usb_4_mic_array $ sudo python tuning.py DOAANGLE
DOAANGLE: 180
Q3: Do you have the example for Raspberry alexa application?
A3: Yes, we can connect the mic array v2.0 to raspberry usb port and follow Raspberry Pi Quick Start Guide with Script to do the voice interaction with alexa.
Q4: Do you have the example for Mic array v2.0 with ROS system?
A4: Yes, thanks for Yuki sharing the package for integrating ReSpeaker Mic Array v2 with ROS (Robot Operating System) Middleware.
Q5: How to enable 3.5mm audio port to receive the signal as well as usb port?
A5: Please download the new firmware and burn the XMOS by following How to update firmware.
Thank you for choosing our products! We are here to provide you with different support to ensure that your experience with our products is as smooth as possible. We offer several communication channels to cater to different preferences and needs.
| Hoạt động | Hướng dẫn chi tiết |
| Sử dụng ban đầu | Kết nối bo mạch với thiết bị chủ (Raspberry Pi, PC Linux/Windows, Mac) qua cổng Micro USB. Thiết bị sẽ được nhận dạng là một card âm thanh USB. |
| Cấu hình phần mềm | Để sử dụng các tính năng nâng cao (BF, DOA, AEC), người dùng cần cài đặt SDK và thư viện của Seeed Studio/XMOS trên thiết bị chủ (thường là hệ điều hành Linux như Raspbian/Ubuntu). |
| Vận hành (DOA/BF) | Vận hành thông qua các lệnh gọi API. Ví dụ: gọi API để thiết lập hướng Beamforming (tập trung micro) hoặc để nhận dữ liệu hướng giọng nói (DOA). |
| Thùng loa/Vỏ case | Khi lắp đặt vào vỏ case, không được che chắn mảng micro (4 lỗ micro) để đảm bảo thu âm đa hướng và hiệu suất của thuật toán Beamforming. |
| Bảo quản | Sản phẩm là một bo mạch điện tử, cần tránh xa độ ẩm, bụi kim loại, và các chấn động mạnh. Đảm bảo nguồn điện USB 5V ổn định. |
Chúng tôi sẽ liên hệ và gửi báo giá theo thông tin mà bạn cung cấp!